How to Assess Asphalt Damage: A Visual Guide
Key Takeaways
- Identifying asphalt damage early can prevent more extensive repairs.
- Different types of damage require specific assessment techniques.
- Regular maintenance and timely repairs extend the life of asphalt surfaces.
- Utilize proper tools and methods to accurately evaluate damage.
- Understanding damage types aids in selecting suitable repair materials.
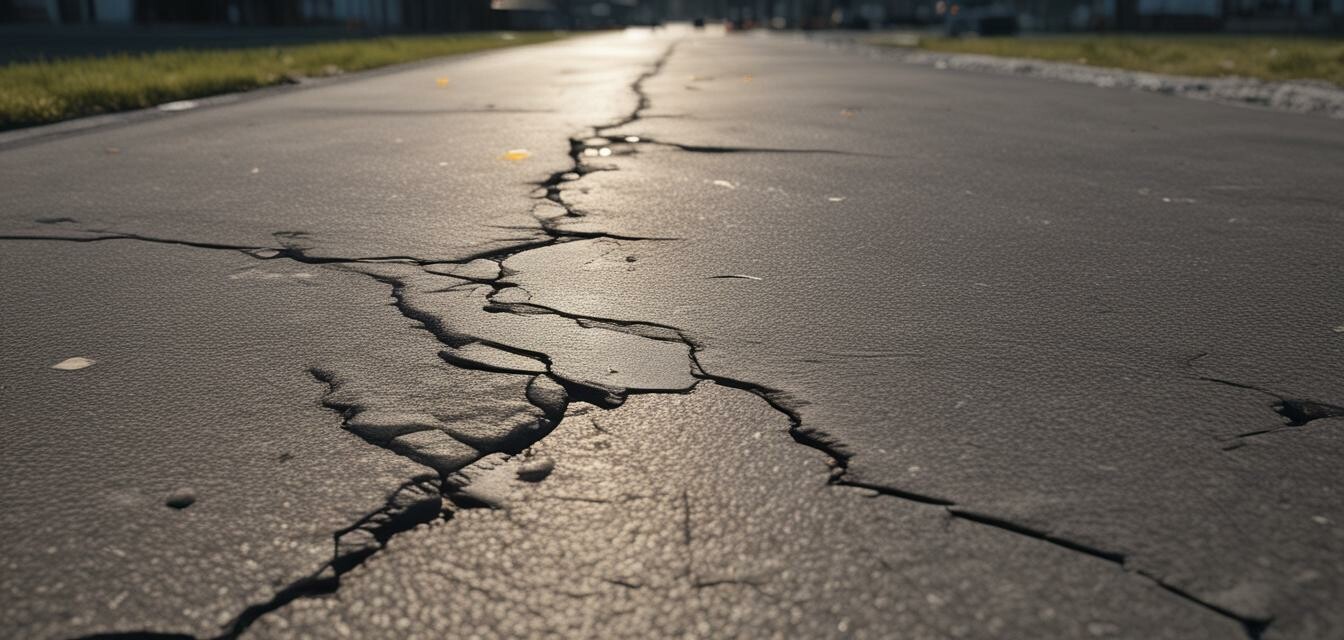
Asphalt surfaces can experience various types of damage over time due to wear and tear, environmental factors, and improper installation. Knowing how to assess asphalt damage is crucial for effective maintenance and repair. This visual guide will help you recognize different asphalt damage types, understand their implications, and determine the best repair strategies.
Recognizing different types of asphalt damage
Identifying asphalt damage begins with visual inspection. Below are common types of damage to look for:
- Cracks: Can develop due to aging, freeze-thaw cycles, or heavy traffic.
- Potholes: Result from water infiltration and freezing temperatures.
- Raveling: Occurs when the surface material starts to break down, exposing aggregate.
- Alligatoring: Characterized by interconnected cracks resembling an alligator's skin, indicating structural failure.
- Surface Erosion: Loss of the top layer of asphalt, reducing durability and appearance.
Visual guide to assessing asphalt damage
1. Cracks
Cracks can appear in various forms:
| Type of Crack | Description | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Hairline Cracks | Narrow, shallow cracks less than 1/4 inch wide. | Seal with crack filler. |
| Medium Cracks | Cracks between 1/4 inch and 1 inch. | Repair with rubberized crack filler. |
| Wide Cracks | Cracks wider than 1 inch, may indicate severe damage. | Consider patching or resurfacing. |
2. Potholes
Potholes can be tricky to assess, as they can deepen quickly:
- Measure the depth of the pothole with a ruler.
- Check for water accumulation, indicating drainage issues.
- Assess surrounding asphalt for further damage.
3. Raveling
Look for loose stones and the loss of aggregate which can indicate raveling:
- Examine the surface for flaking or peeling.
- Check for a gritty texture when walking on it.
- If conditions are severe, a full resurfacing may be necessary.
4. Alligatoring
Alligatoring signifies structural issues:
Pros of identifying alligatoring
- Signals underlying problems before total failure.
- Allows targeted repair to enhance durability.
Cons of ignoring alligatoring
- Can lead to large-scale replacement of asphalt.
- Increased costs due to major repairs.
5. Surface Erosion
Erosion is often a result of inadequate surface sealing:
- Look for a worn appearance and exposed aggregate.
- Check for increased water infiltration during rain.
- Consider resealing the surface to prolong life.
Assessing the extent of damage
Once you identify the different types of asphalt damage, assess the extent to create a repair strategy.
1. Document your findings
Take photos of the damage and record measurements.
2. Consult with experts
If damage is extensive, contact professionals for advice on repair options. Professional equipment can greatly enhance repair results.
3. Determine the best course of action
Based on the assessment, decide whether to fill small cracks, patch potholes, or do a complete surface overlay. Check out our section on buying guides for tips on selecting the right materials.
Conclusion
Regularly assessing asphalt damage is key to maintaining a safe and aesthetically pleasing pavement. By familiarizing yourself with the signs of damage and developing a systematic approach to inspection and repair, you can extend the life of your asphalt surfaces. For further resources, explore our instructional guides for comprehensive information on asphalt care.