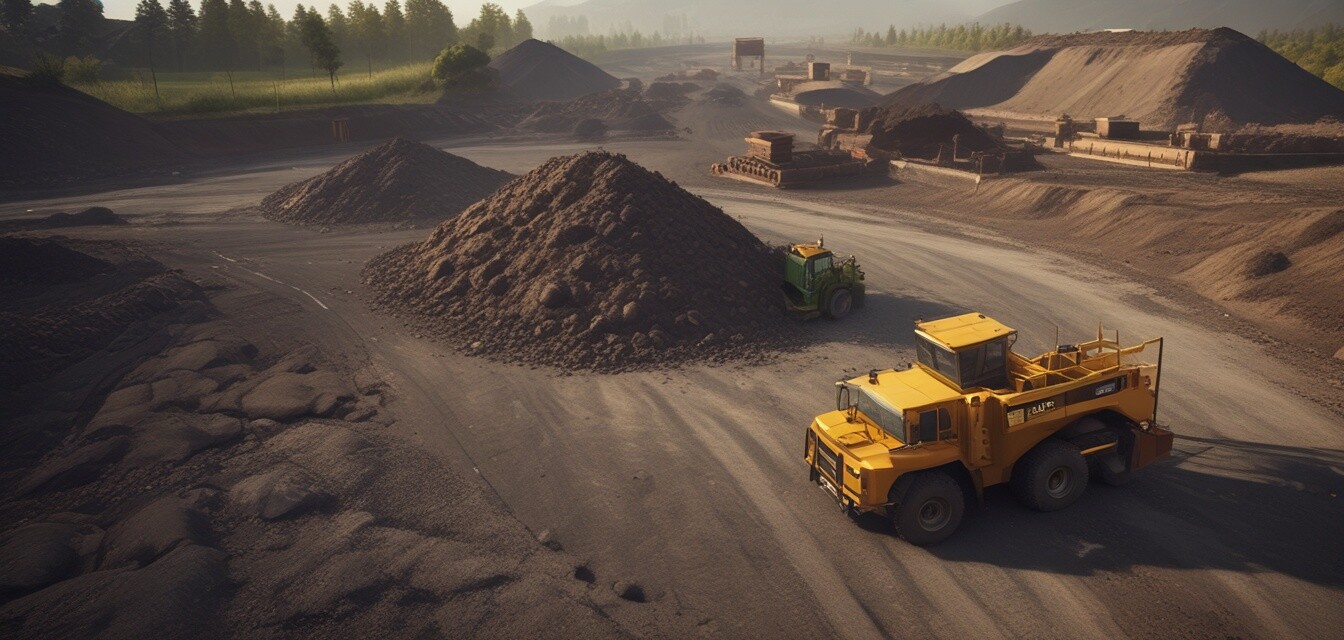
The process of asphalt recycling: A detailed overview
Key Takeaways
- Asphalt recycling involves reusing old pavement materials to create new asphalt, promoting sustainability.
- Benefits of asphalt recycling include cost reduction, reduced environmental impact, and efficient resource utilization.
- There are several methods of asphalt recycling, including hot-in-place recycling and cold recycling.
- Understanding the recycling process can lead to improved paving practices and better project outcomes.
As asphalt pavement deteriorates over time, the need for effective recycling methods becomes increasingly paramount. Understanding the asphalt recycling process is essential for contractors, DIY enthusiasts, and those invested in sustainable paving practices. This article will provide you with a comprehensive overview of the asphalt recycling process, including its numerous benefits, methods, and applications in modern paving projects.
Benefits of asphalt recycling
Asphalt recycling offers numerous advantages that extend beyond financial savings. Here are some key benefits associated with the recycling process:
- Cost savings: Recycling asphalt can significantly reduce the overall expenses associated with paving projects by decreasing the need for new materials.
- Environmental impact: Utilizing recycled asphalt helps decrease waste sent to landfills and lowers the demand for new resources, resulting in a reduced carbon footprint.
- Enhances road quality: Recycled asphalt can perform as well, if not better than, virgin materials when appropriately processed and applied.
- Energy efficiency: The energy required for recycling asphalt is significantly lower than producing new asphalt, leading to improved sustainability.
Methods of asphalt recycling
There are several effective methods for asphalt recycling, each catering to different project needs and conditions. Below is a brief overview of the most common methods:
| Method | Description | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Hot-in-place recycling | This method heats and reuses the existing pavement without removing it. It involves milling the top layer, rejuvenating it, and then laying it back down. | Ideal for surfaces showing moderate distress, such as cracks and surface wear. |
| Cold recycling | Cold recycling involves milling the asphalt and mixing it with additives to create a new material without heating it first. | Suitable for heavily worn pavements and areas with severe structural issues. |
| Full-depth reclamation | This process recycles the entire asphalt pavement, often incorporating a binder and often a new surface layer to enhance performance. | Used for deeply distressed or failed pavements. |
| Recycled asphalt pavement (RAP) | RAP is asphalt that has been reclaimed and reused as aggregate in new asphalt mixes. | Can be incorporated into various asphalt mixtures for both resurfacing and new construction. |
Applications of recycled asphalt
The versatility of recycled asphalt allows its use in various applications, ranging from road construction to repairing existing surfaces. Here are some key applications:
- Road construction: Recycled asphalt is widely used in both new pavement construction and for resurfacing existing roads.
- Pavement maintenance: Recycling can extend the life of asphalt pavements through various maintenance techniques, including patching and crack sealing.
- Parking lots: Using recycled asphalt for parking lots is cost-effective and environmentally friendly.
- Sports surfaces: Some sports facilities utilize asphalt mixtures that include recycled elements for improved performance and sustainability.
Best practices in asphalt recycling
To achieve optimal results in your asphalt recycling efforts, consider implementing the following best practices:
- Conduct thorough evaluations of the existing pavement condition before deciding on a recycling method.
- Ensure proper equipment is used for it to be efficient.
- Follow local regulations and guidelines regarding recycled asphalt usage.
- Perform regular maintenance and inspections of recycled asphalt surfaces to ensure longevity and performance.
Conclusion
Asphalt recycling is a vital process that offers numerous benefits, including cost savings and a reduced environmental footprint. With various methods available to suit different project requirements, utilizing recycled asphalt can lead to improved paving practices and successful project outcomes. By understanding the recycling process and embracing best practices, paving contractors and DIY enthusiasts alike can contribute to a more sustainable future in asphalt paving.
Pros
- Cost-effective paving solutions.
- Environmentally friendly approach to asphalt applications.
- Improved pavement quality and longevity.
Cons
- Some methods may require specialized equipment and expertise.
- Quality control is essential to ensure performance.
Further reading
For additional resources related to asphalt and paving, check out the following articles: